On This Page
- What is Radon?
- When to test for radon at home
- How to get a radon test at your home
- Radon explainer videos
- Radon in Tompkins County
- Information for radon professionals
What is Radon?
Radon is the leading cause of lung cancer among nonsmokers. You can’t see, smell or taste radon, but it could be present at a dangerous level in your home. The only way to know if your home has high radon levels is to test it.
Radon is a naturally occurring, radioactive gas found in soil and rock that gets into the air you breath. It seeps into buildings through cracks in the foundation, walls, and joints. It can get into any type of building--homes, offices, and schools. The greatest risk for exposure is where you spend most of your time – usually at home.
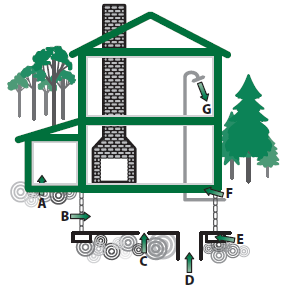 Major Radon Entry Routes
Major Radon Entry Routes
- Cracks in concrete slab
- Pores and cracks in concrete blocks
- Slab-footing joints
- Exposed soil, as in sump
- Cracks between poured concrete (slab) and blocks
- Loose fitting pipes
- Water
When to Test for Radon at Home
- Every five years or every two years if you have a radon mitigation system to make sure it’s working properly.
- When buying a home and after major renovations. During a real estate transaction, hire a certified radon measurement professional for testing. Be sure that the analysis of the radon test is performed by a company approved through the State's Environmental Laboratory Approval Program.
- Within 30 days of installing a radon mitigation system.
Information about testing your home for radon is in the How to Test section below.
Understanding Your Test Results
NYS DOH recommends fixing your home if the results of radon tests show levels of 4 picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L) or higher. With today's technology, radon levels in most homes can be reduced to 2 pCi/L or below. You also may want to consider fixing if the level is between 2 and 4 pCi/L.
Fix a Radon Problem
A radon reduction system can reduce radon levels in your home by up to 99% and average cost is about $1,500. If your home has elevated levels of radon, contact a certified radon mitigator (see Resources section, below).
Building Homes To Keep Radon Out
New construction methods keep radon out of the home by sealing soil gas entry points, by preventing radon gas from entering the home and by venting to release radon gas outdoors. Installing a radon reduction system during construction is easier and less expensive than installing a system after the house is completed. Every new home should be tested, even if it was built to be radon resistant. If radon levels are still at or above 4 pCi/L, a certified mitigator may activate the system by installing a fan.
How to get a radon test at your home
 In Tompkins County, free radon home-test kits are available via Whole Health's Healthy Neighborhood Program.
In Tompkins County, free radon home-test kits are available via Whole Health's Healthy Neighborhood Program.- Homeowners in New York State can order one free radon test kits (while supplies last) or obtain low-cost test kits through New York State. Visit health.ny.gov/radon for more details.
- Radon home-test kits can be purchased at a variety of home-improvement retailers, such as ACE Hardware Store, Lowe’s, Home Depot and Walmart.
- Certified Radon Testers: Collect air samples at your home.
- Analyzing collected sample: Anyone who analyzes and provides the results of those tests must hold NYSDOH Environmental Laboratory Approval Program certification.
- Radon mitigation: Radon reduction systems and guidance for selecting a qualified contractor in NYS.
- U.S. EPA's Consumer's Guide to Radon Reduction.
Radon Explainer Videos
from the HUD Exchange
Radon Awareness and Planning
Radon Testing
Radon Mitigation
Radon in Tompkins County
Radon Test Results By Town
The New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH) Radon Program provides short-term charcoal radon test kits and radon test kit analysis to residents. The radon test results are provided to the individual home owner and the Radon Program. All testing data is entered into a NYSDOH database. Levels of 4 picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L) or higher should be addressed.
In Tompkins County, free radon testing kits are available from Whole Health's Healthy Neighborhood Program.
Radon levels by town.
Wadsworth Center Maps
Right click on image to "Open image in a new tab". Use links below the maps to open original source.
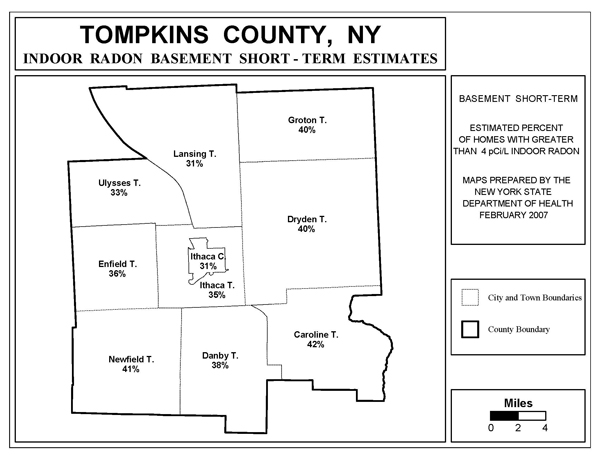
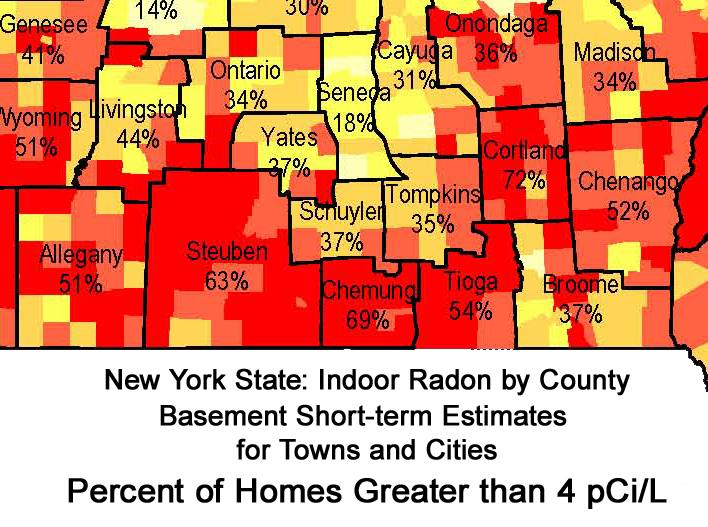
Tompkins County map | New York State map (all counties) | Wadsworth Center radon page
Information for Radon Professionals
The American Association of Radon Scientists and Technicians and the American National Standards Institute (AARST/ANSI) have developed National Radon Standards for radon testing and mitigation. These are the currently accepted standards and supersede previous EPA standards for radon.
Find Regional Radon Training Centers for continuing education.
Radon testing firms and mitigators must report testing results to the DOH. View Title 10 NYCRR 16.130 Radon Testing and Reporting for laws and regulations.
For Radon Testing Firms/ELAP Certified Laboratories:
Part 16 of the New York State Sanitary Code requires the reporting of County or Zip Code and number of measurements. You are only required to report the name of the laboratory in cases where the laboratory report the radon results to DOH.
For Radon Mitigators:
Part 16 of the New York State Sanitary Code requires the reporting of County or Zip Code and number of mitigations.
Please email radon@health.ny.gov or call (518) 402-7556 to request the Excel spreadsheet template for reporting your data.
Completed reports can be submitted via:
- Email to radon@health.ny.gov
- U.S. Postal Service to:
Center for Environmental Health
Bureau of Environmental Radiation Protection
Empire State Plaza-Corning Tower, Room 1201
Albany, New York 12237
National Radon Action Plan (RADONLEADERS.ORG)
Source of content for this page: NYS Department of Health, Radon (Revised January 2024).
This page created: 1/19/2024.

